Chemical substances are indispensable for people to lead comfortable and fulfilling lives. Failure to properly manage chemical substances, however, can result in accidents that put human health and ecosystems at enormous risk. In addition to compliance with related laws and regulations, the Lion Group strives to ensure the strict management of chemical substances at all stages from product development to use and disposal in accordance with its own independent standards.
Based on the spirit of the Lion Group Charter for Corporate Behavior, the Group has established the Chemical Substance Management Policy. This policy was formulated in light of international trends in chemical substance management and is aligned with the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM). The policy stipulates that we will strive to implement sound management of chemical substances throughout their lifecycles, minimize significant adverse impacts on the environment and human health, and promote communication.
Group-Wide Management of Chemical Substances
The types and amounts of chemical substances used in products are determined at the product development stage, with consideration given not only to enhancing product performance, but safety and environmental impact.
Based on the Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc., Lion notifies the relevant authorities of the use classifications and volumes of all the general chemical substances and priority assessment chemical substances it manufactures or imports (with exceptions based on the provisions of the Act, such as for substances manufactured or imported in quantities of less than one ton per year).As needed, our chemicals departments also notify the relevant authorities of the use classifications and volumes of small-volume and low-volume new chemical substances it manufactures or imports. We will continue to gather information about the volumes and uses of manufactured or imported chemical substances and file proper notifications.
Our chemicals departments register chemical substances as required under the EU’s REACH*1 chemical substance management system.
*1 REACH: Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals
Our chemicals departments and Lion Corporation Korea pre-register and register chemical substances under K-REACH.*2
*2 K-REACH: The common name for South Korea’s Act on the Registration and Evaluation of Chemicals
Going forward, calls for the improvement and reinforcement of chemical substance management will grow. Accordingly, we aim to continue as well as to step up the filing of proper notifications and management of emissions volumes as required under volatile organic compound (VOC) regulations, the Water Pollution Prevention Act and the Act on the Assessment of Releases of Specified Chemical Substances in the Environment and the Promotion of Management Improvement.
The PRTR (Pollutant Release and Transfer Register) system is a scheme for collecting, compiling, and publishing data on the degree to which a wide variety of potentially harmful chemical substances are released into the environment from what sources, or are transported off of production sites through waste disposal.
The Company’s emissions of PRTR-designated substances have remained at 2 to 3 tons since 2019.
PRTR-Designated Substance Emissions
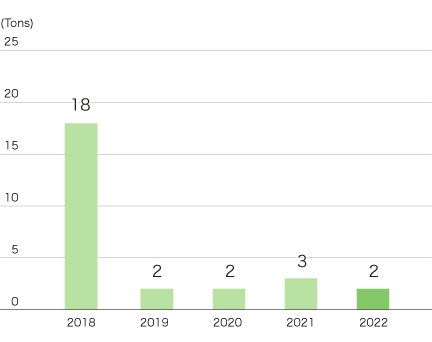
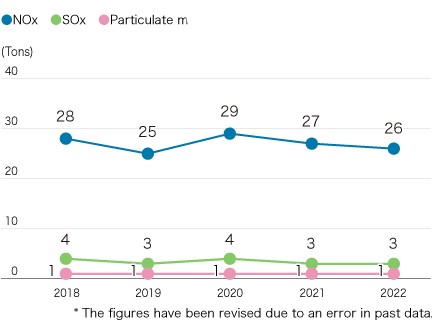
Lion implements initiatives to reduce emissions of chemical substances that cause air pollution, including nitrogen oxides (NOX), sulfur oxides (SOX), particulate matter and VOCs. The Air Pollution Control Law designates emissions standards by type of substance and by type and scale of emitting facility, and many regional governmental bodies have established additional regulations by ordinance. In addition to complying with such laws and ordinances, each plant has formed strict agreements with local municipalities and established strict voluntary standards, in accordance with which we strive to prevent pollution. Furthermore, we are working to reduce emissions by such means as improving the efficiency of production processes and utilizing environmentally friendly equipment, such as nitrogen and sulfur scrubbers.
Emissions of Nitrogen Oxides (NOX), Sulfur Oxides (SOX) and Particulate Matter
VOC Emissions
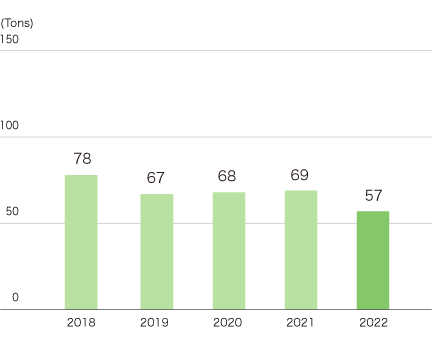
A maximum limit on COD*1 of 160mg/L (and a daily average of 120 mg/L) has been set by law as a uniform standard within environmental standards related to water pollution per the Water Pollution Prevention Act and Sewerage Act. Lion meticulously complies with these regulations in its business activities. Furthermore, Lion aims for even stricter wastewater quality management, and some of our operating sites have formed agreements with local governments to maintain a COD limit stricter than the uniform standard. By stabilizing the operations of the wastewater treatment facility, performing regular maintenance and improving treatment methods, we are working to further reduce COD in wastewater emissions.
*1
COD
Chemical oxygen demand. An indicator of water contamination. Indicates the amount of oxygen that will be consumed in the oxidization and decomposition of the organic matter content of the water.
Lion prepares safety data sheets (SDSs)*2 on its chemical products and provides them to its customers. We also receive SDSs on all the raw materials we use from our suppliers. These SDSs are listed in a database to be used effectively.
*2
SDSs
Safety data sheets. Documents providing information about the environmental impact of, safety precautions regarding and the appropriate handling of chemical products, aimed at preventing accidents caused by chemical substances.
In case of an accident during the transportation of raw materials or intermediate products, Lion provides information to carriers about emergency response by distributing and attaching yellow cards and container yellow cards* to shipments.
*
Yellow cards and container yellow cards
Yellow-colored emergency contact cards providing information about the properties of and emergency response methods regarding chemical substances in case of leaks of other issues during transportation. Yellow cards are for carriers to keep with them during transportation, while container yellow cards are attached to the containers in which chemical substances are stored. Both are prepared based on voluntary industry standards determined by chemical companies.
After being used, the surfactants in detergents and other products are discharged into the environment. Four times a year, Lion takes part in the Japan Soap and Detergent Association’s environmental monitoring and risk assessment of four types of surfactants in rivers near Tokyo and Osaka in order to ensure that the impact of these substances on local ecosystems is minimal.
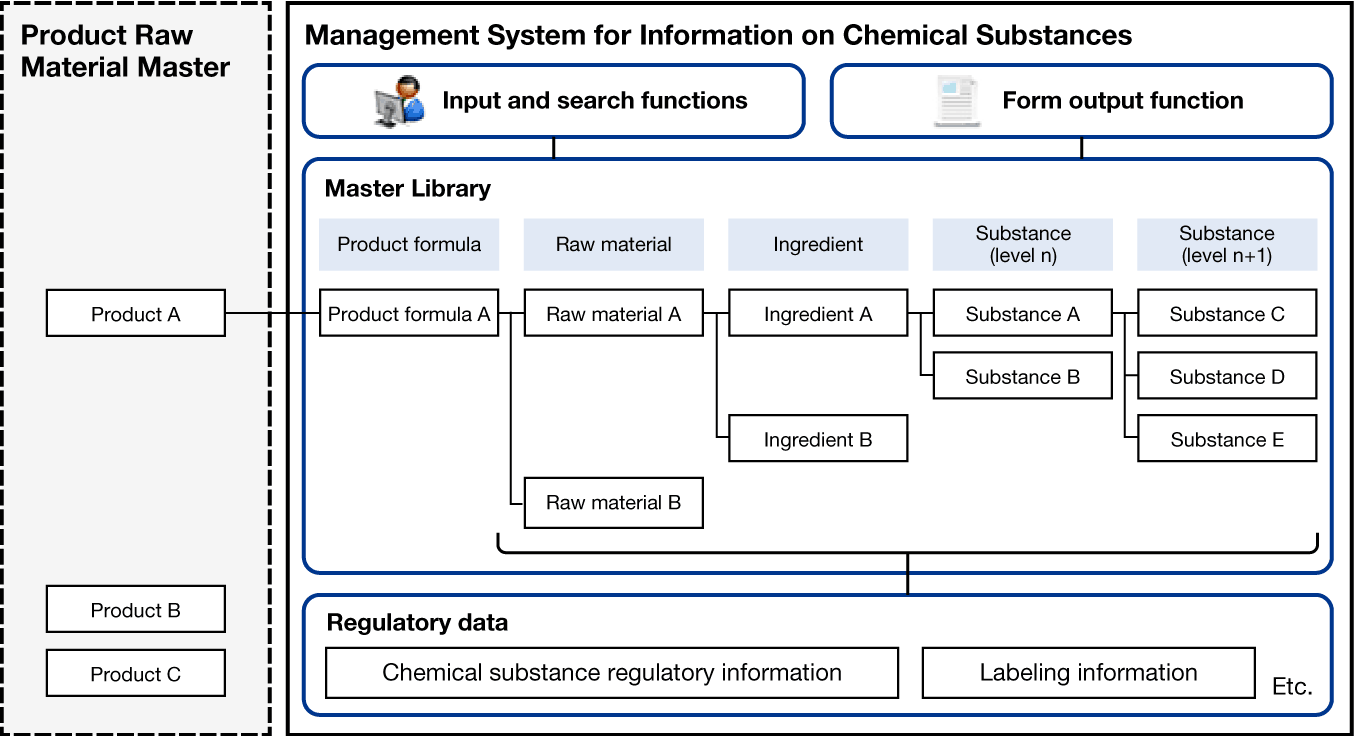
Since January 2018, Lion has been rolling out a Management System for Information on Chemical Substances at its purchasing departments and research and development sites, including those of domestic affiliated companies, to reinforce the proper use of chemical substances. We use this system for the management of raw materials and the chemical substances contained in products.
The system comprises a database of raw materials and product formulation data, a database of regulatory data, and product formula development support functions. The adoption of the system has reinforced our framework for ensuring legal compliance regarding chemical substances used in products during product development across all our business fields. In addition, the system’s accumulated data allows employees to instantly search through the chemical substances contained in products that have been released. This has helped enhance data management, secure traceability and reinforce our ability to ensure compliance.
In addition, as a member of the Joint Article Management Promotion-consortium (JAMP), we ensure that our chemicals departments provide customers with information on the chemical substances contained in products using JAMP’s chemSHERPA common format.*1 We also provide information on REACH SVHCs.*2
*1 chemSHERPA: A common scheme for the transfer across a supply chain of information about chemical substances contained in products.
*2SVHC (substances of very high concern): Substances that are candidates for inclusion in REACH Annex XIV as substances subject to authorization. “Authorization” here refers to that which is indicated in the name REACH, which stands for Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals.
In 2021, the use of nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPEs) in the EU was restricted by EU REACH.*1 Furthermore, Japan is set to designate NPEs as Class II Specified Chemical Substances under Japan’s Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc. in 2024. Lion has already discontinued the use of NPEs and completed the process of replacing them with substances that have a lower environmental impact.
The restriction of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was declared under the POPs Convention*2 in 2019. Furthermore, Japan designated PFOA a Class I Specified Chemical Substance under the Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc. in 2021, with its manufacture and import being prohibited in principle. In response to this, Lion conducted a survey using the Management System for Information on Chemical Substances and an investigation of raw material manufacturers, thus discovering that some raw materials in our chemicals department contained PFOA as an impurity. However, we have completed the process of replacing such raw materials with those that do not contain PFOA prior to the Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and Regulation of Their Manufacture, etc. coming into effect.
*1 REACH: Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals
*2 The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs):A multilateral environmental agreement that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organic pollutants.